What Is Combined Assurance Model?
Discussing Combined assurance model requires understanding of the following:
- what assurance means,
- roles of the three lines of defense in providing assurance,
- current issues with the assurance delivery,
- how to adopt combined assurance to resolve the current issues with the assurance delivery,
- the situation in Nigeria and a call to action for the organizations in Nigeria.
Assurance is defined as the supervisory reviews, monitoring and auditing activities performed by the parties that are not directly involved in business transactions initiation, documentation, approval and completion. The primary objectives for the assurance activities are to ensure that the following organizational needs are met:
- company policies and procedures are followed, and the applicable legal and regulatory standards are conformed with,
- independent insight, unbiased opinion and valuable advice to the company management and governorship teams are provided,
- corporate vision, mission, value propositions, goals and objectives, strategies, funding and resourcing requirements are understood and met,
- adequacy and effectiveness of the assurance functions which include risk management, internal control, regulatory compliance and governance functions, processes and policies,
- root causes of all the deficiencies observed are identified, actionable solutions provided and applied to resolve the issues
- improvement opportunities are enhanced and optimized,
- accuracy, completeness and validity of the data and information generated across the organization to enhance strategic decisions and actions,
- stakeholders’ expectations and interests are understood and that the stakeholders’ interests that do not conflict with the interest of the organization are met,
- overall performance of the management and governance levels are aligned to the corporate strategies, goals and objectives.
The assurance performance is done through the use of the following mechanisms:
- review of reports,
- inspection of documents,
- analysis of financial and non-financial data and transactions,
- stakeholders’ interview,
- forum discussions,
- survey administration,
- benchmarking studies and
- other methods subject to the peculiarities of the specific organizations involved.
The assurance delivering lifecycle involve many iterative stages which include the following:
- Stage 1 – engagement planning which may be strategic, annual or operational planning,
- Stage 2 – field work execution, working papers documentations and discussion of observation with the auditees,
- Stage 3 – preparation of the assurance reports and presentation to the principal end users which primarily include the executive management, boards and board committees,
- Stage 4 – incident tracking, follow-up monitoring, resolutions and reporting,
- Stage 5 – performance quality improvement through regular internal self-assessment reviews and periodic independent /external assessment reviews.
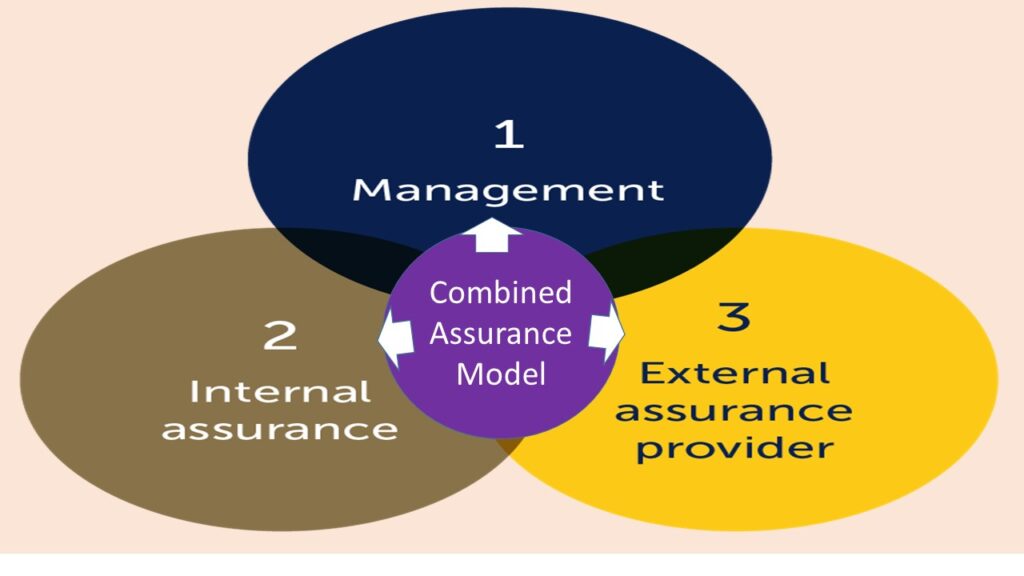
Assurance providers have been categorized into three levels generally called ‘the three lines of defense (3LoD)”. However, some others perceive the categories to be more than three.
Presented below are the three lines of defense categories and examples of the compositions for each of the categories.
- level 1 – first line of defense are the monitoring and supervisory reviews performed by the members of the front line or core business functions such as the Executive Management Committee, (EXCO), Capital Project Implementation Committee., Internal Departmental Review Subcommittee and inter-department review meetings.
- level 2 – second line of defense are the semi- independent assurance providers that technically report directly to the executive management and perform continuous control monitoring reviews, risk and control standard setting and coordination. Members comprise Risk Management, Ethics and Regulatory Compliance, Internal Control, Quality Management, HSEQ, Information Security monitoring, Physical Security, Quality Control and Assurance.
- Level 3 – third line of defense are the full independent assurance providers that technically report directly to the board committees. Members comprise the Internal Auditors and external assurance providers such as External Auditors, Independent Asset Valuers, External Rating Agencies. Cyber Security Vulnerability Assessors and Regulatory Supervisors.


Very insightful!
A Combined Assurance Model (CAM, if properly deployed will eliminate waste of resources, optimise assurance cost and ultimately a plus to the bottom line!