Responsibilities For Risk Prediction
The responsibility for risk prediction, mitigating control design and operations within the First Line of Defense (1stLOD) functions rest directly on the risk owners within the first line of defense functions. For example, the head of marketing department is the owner of the risks and controls relating to the marketing department and processes while Chief Finance Officer is the risk owner for risks and controls relating to the finance and accounts department and processes.
The members of the second and third lines of defense (2ndLOD and 3rdLOD) functions, particularly, risk management, internal control, regulatory compliance and internal audit can only play coordination, advisory and assurance roles relating to risks at First Line of Defense functions to prevent self-review threats.
Coordination and advisory means that the internal audit, risk management, internal control or regulatory compliance can facilitate risk prediction discussion forums, provide sample documentation templates, standard guidelines and clarifications to the risk owners to enable greater understand and insights on what to do.
The second and third lines of defense ((2ndLOD and 3rd LOD) functions only have direct responsibility for the risks and controls within their own departments and processes which primarily center around conflict of interest and detection risks. Leading practices requires that the assurance over the risks and controls associated with the second and third lines of defense functions should be done through independent quality assessment reviews by knowledgeable professionals within or outside the company, but not from the specific risk assurance department 2ndLOD and 3rd LOD functions owning the risks.
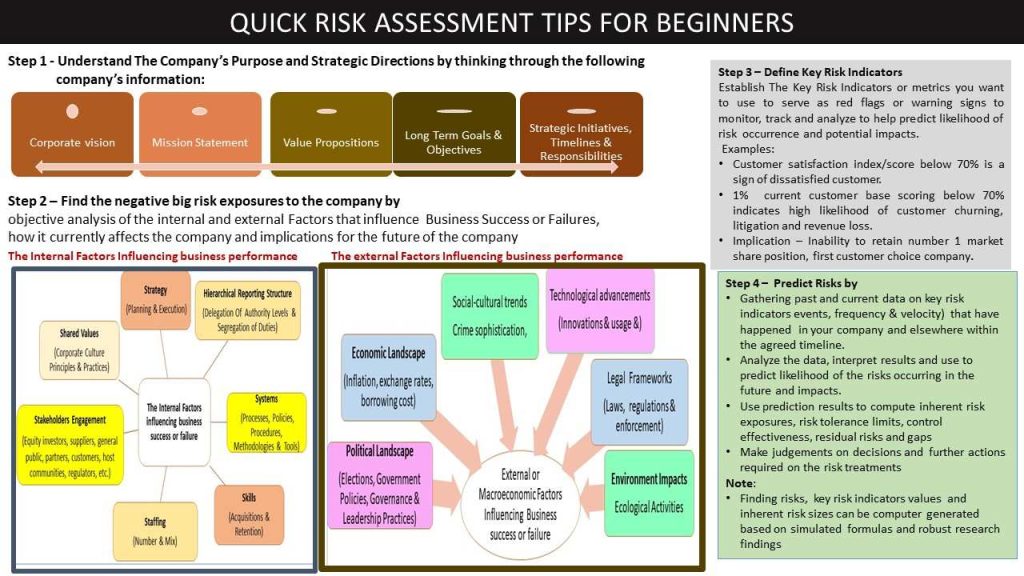
How To Find The Right Risks
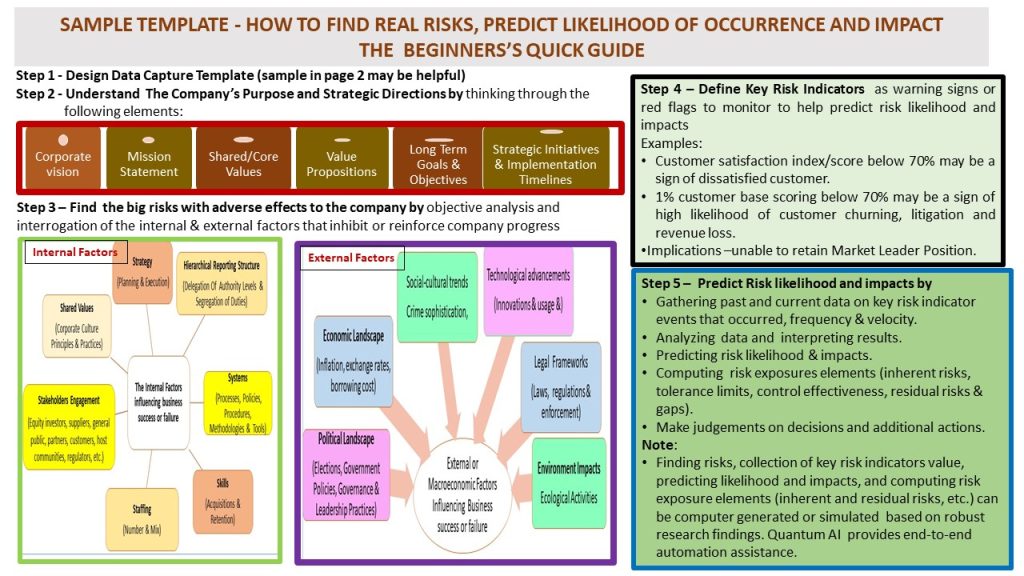
The diagram below provides a high level summary of the key activity steps to be performed in finding and predicting risks.
In risk prediction, finding the right risk events must be completed before predicting the likelihood of the risk occurrence and potential impacts. The Top-down and Bottom-up models are the most popular approaches often used in finding and predicting risks. The input source data that are used for predicting the risks can be derived from any of the following:
- real historic data collected over time from past events that occurred within or outside the company or
- artificially system generated data simulated based on robust research findings or
- a combination of real historic life events and artificially generated system simulated data
Completing the top-down and bottom-up activities and generating the input source data to be used in the risk prediction can be done through manual or semi-automated or end-to-end automated processes. The application of Quantum Artificial Intelligence in completing the processes end-to-end brings significant benefits – efficiency, cost savings, high volume, accuracy, accessibility, security, etc.
How Top-Down Approach Works – Finding and Predicting Risk
The Top-down approach is risk based and focused on the bigger picture issues to the organization. It starts by
- Understanding the primary purpose of the company and strategic directions
- identifying the critical top level internal and external events, conditions and actions that can threaten the achievement of the company’s overall purpose and strategic directions
- Predicting the likelihood that the critical top level internal and external events, conditions and actions will occur and the potential impacts on the achievement of the company’s overall purpose and strategic directions.
Sourcing for the right information to achieve items 1 to 3 above will require productive engagement with the stakeholders, desktop reviews of the relevant company’s strategic internal documents, robust external research and survey questionnaire administrations. The brief description below provides more insights.
- Productive engagement with the stakeholders involves scheduling and holding interviews or focus group forum discussions or questionnaire administrations to the top level business leaders (executive management and board), senior management (heads of departments), risk owners, key customers and service providers to obtain their perceptions of the current situation in the company given the internal and external factors influencing business performance, and their perspectives for the future of the company.
- Desktop reviews of the relevant strategic internal documents involve gathering critical documents such as corporate strategy. board and Executive management committee (EXCO) minutes of meetings, monthly, quarterly and annual management accounts report, Audited financial statements, regulators’ supervisory visit reports, annual budgets and departmental position reports
- Robust external research involves understudying external research findings from credible organizations on the internal and external factors influencing business performance such Industry Benchmarks from global auditing and consulting firms like PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC), Global Risk Reports from World Economic Forum (WEF) and Association of Certified Fraud Examines (ACFE), Global and Domestic Macroeconomic outlook from World Economic Forus and Lagos Business School (LBS) research publications..
good tip is to know that potential risk events are always hidden in the internal and external factors that influence company performance as depicted in the diagram below.
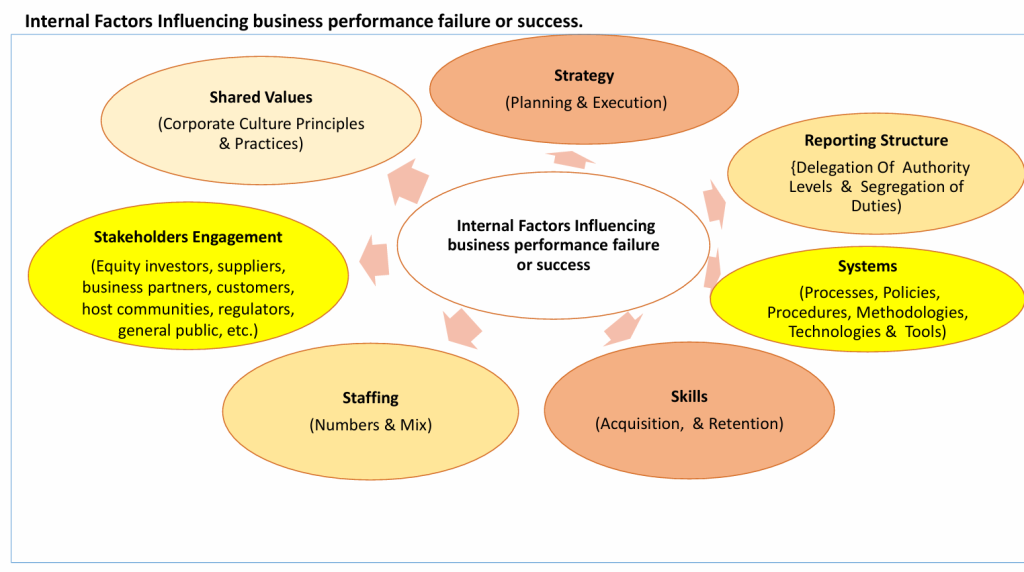
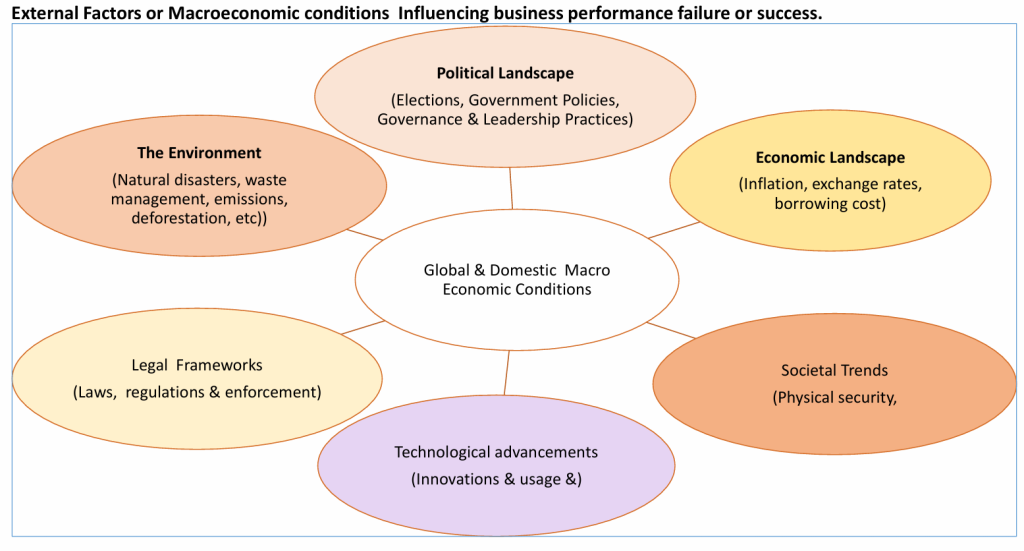
The critical analysis and interrogations of the above internal and external factors and proper interpretation of the results will provide robust and objective insights and perspectives on the company’s purpose and strategic directions, the company’s strengths, weaknesses (vulnerabilities), opportunities, threats, key risk indicators for tracking the extent of influence on the achievement of the company’s purpose and strategic directions.
- The company’s purpose and strategic directions are derived from analysis of the company’s vision, mission, shared values, value propositions and long term, medium term and long-term goals and objectives.
- The Strengths are good practices within the company that increases the company’s resilience to withstand threats and continue to survive, succeed and grow in the face of serious challenges and tough business environment.
- The Weaknesses are the vulnerabilities or bad practices that increase the organization’s susceptibility to falling to the threats, thereby limiting the company’s ability to achieve its purpose and strategic directions.
- The Opportunities are improvements or benefits that the organization needs to explore to increase value addition
- The Threats are future events, persons, objects, behaviours, conditions, actions and things whose occurrence can hurt the company by causing damage, injury, delay or loss to the company’s finance, operations, physical assets, projects, people and business relationships and ultimately lead to the company’s inability to achieve its fruitful purpose and strategic directions.
- The Key Risk Indicators (KRI) are derived from the RedFlags or a warning sign established at the strategic and operational levels based on business needs, stakeholders’ expectations, industry best practices, legal and regulatory compliance requirements and resourcing availability.
The attached template provides practical tips on how to use top-down model to find strategic risks, predict likelihood of occurrence and impacts, and link the results to the company’s purpose and strategic directions.