The fraud risk assessment activities for consideration by the internal auditors.
As depicted in the internal audit life cycle presented above, the phase 1 of the internal audit lifecycle is the “Risk and Audit Universe Validation”. This phase 1 – “Business Need, Risks and Audit Universe Validation” involves gathering basic information about the company and using the information to identify fraud indicators. The key documents and information for gathering include the following:
- Minutes of the Executive management, board and board committee meetings and registers
- Corporate governance framework, ERM framework, Internal control Framework and associated charters
- Audit universe items to be used for internal audit planning,
- company’s vision, mission, core values, value propositions, strategic goals and objectives, business needs and stakeholders’ expectations
- potential risk exposures including the fraud risks.
- Historic incident tracking records of loss events, near misses, root causes, consequences, overall impacts and closure status.
- Fraud complaints and whistle blower reports.
- Transaction pools of reversals, manual interventions/entries and automatic generated transactions.
- Postdated and backdated transactions history.
- Month-end and year-end and late postings history including those done after cut-off periods.
- Unusual transactions such as off time postings, above limits, below baselines, negative and positive postings where the opposite is the acceptable norm.
- Customers and supplier complaints Registers
- Suggestion box reports.
- Human Resources policies documents and staff files
- Ethics and Code of Business Conducts with employee certifications files for board of directors, management and third-party service providers,
- Media and communications processes, policies, procedures and stakeholders communication files and company news letters, etc
- Sales and marketing policies, processes and procedures,
- Contract agreements with third part service providers and list of projects awarded for the period.
- Procurement policies and procedures and standard operating procedures
- Annual budget and corporate strategic plan
- Performance management procedures, policies and processes
- Industry reports including external surveys, research and white papers, professional virtual community discussion forums, media news, reviews and public comments to gain insight into the global and domestic market and industry trends, implications and required responses.
Note that the focus of the information gathering is about fraud and abuse in the company. Gathering the information above requires using different methods which include combination of the following:
- observation of individual lifestyles (behaviors, attitudes, perceptions, perspectives and actions),
- interviews with key stakeholders,
- desktop reviews of the available documents,
- data analytics – analyzing historic business transactional data using data simple and specialized automated analytics tools
- research – gaining insights into global and local trends through research and industry surveys
Observations may take time and lots of resources and human efforts, therefore may be very expensive to use for the internal audit planning except for special projects such as fraud investigation. It is important to note that fraud investigation is different from fraud risk assessment and never part of fraud risk assessment.
Interview method involves engaging with the business leaders including CEO, CFO, Board and Audit Committee Chairs with discussions on issues specific to fraud and abuse to understand their perceptions of the current situation and perspectives for the future. Also interviewed are other stakeholders including some selected executive and non-executive directors of the board and senior management to understand the tone at the top and mood at the middle. It is also important to interview a few selected operational staff to understand the buzz at the bottom whether negative or positive.
Desktop Reviews involves reviewing some specific fraud related documents, business processes, policies, procedures and guidelines such as code of conducts and business ethics, human resources management files such as hiring and retention policies and some selected staff files, employee and stakeholder communications. documents and reports, This will help the interna auditors to assess management’s general attitudes towards fraud from top to bottom levels..
Data Analytics method involves reviewing historic data on fraud and abuse cases through manual or automated methods either on sample basis or whole population to understand the trends, root causes and closures adopted by the business. Use of manual methods , simple data analytics software like spreadsheets and sample selections are best fit where the volume of business operations is small with limited or no automation. In a medium and large sized business with high volume of transactions, use of specialized data analytics software such as ACL, SPSS and others makes it easy and fast to sieve through the entire data population within few minutes with high precision accuracy.
The data and information gathered from the above sources and documents reviews will be analyzed and the findings will help the internal auditor to achieve the following:
- gain broad overview of the likelihood and magnitude of the fraud risk exposures in the business,
- understand the general attitude towards fraud risks including ethics and integrity at all levels in the organisation, commonly known as tone at the top, mood in the middle and buzz at the bottom.
- know what appropriate audit decisions and actions to take for the completion of the subsequent audit phases (phases 2 to 5). Some of the specific decisions and actions include the following:
- audit scope of work coverage for completion during audit field work execution phase,
- nature and type of key controls to focus testing during audit field work execution,
- work timing and duration, – expected duration, start and completion time,
- audit priorities, testing techniques and procedures
- competency levels requirements and whether special and general skill sets will be required, the staffing numbers and sourcing options,
- other resource requirements including finance, mobility, etc.
- reporting templates, distribution lists and channels.
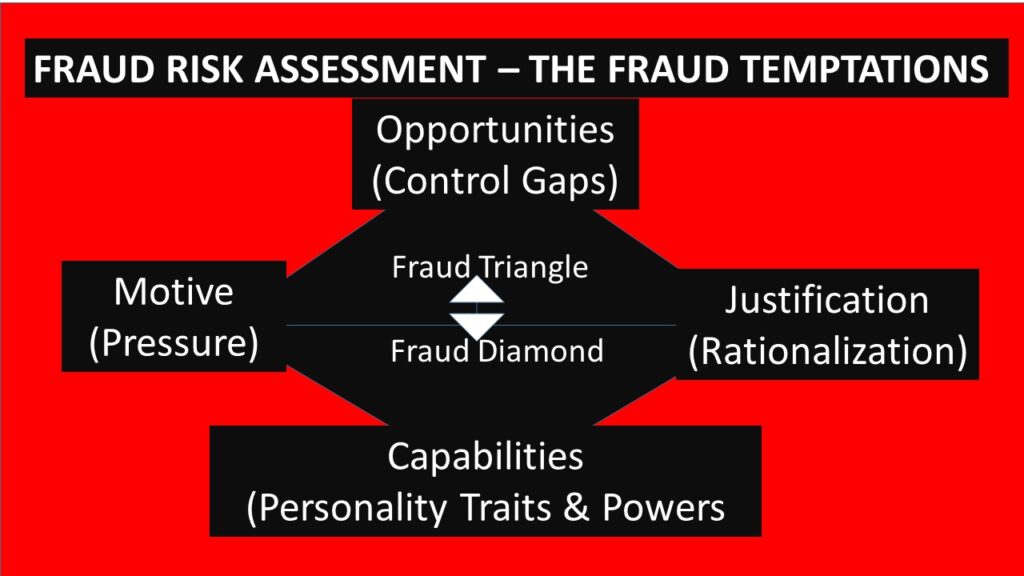


The blog touched relevant knowledge elements but it is too long. Concise blogs pass messages quicker.
Dear Edu
Thanks for the comment. Your recommendations noted.