How Nigeria has adopted the international and regional conventions against fraud and abuse.
As Nigeria is a signed member of the United Nations and some other regional conventions, various legislations and regulatory provisions on combating frauds and abuses have been enacted. The provisions can be found in some of these documents:
- The Nigerian Constitution,
- Criminal Code,
- Penal Code,
- The Companies and Allied Matters Act (CAMA)
- The Money Laundering (Prohibition) Act
- The Economic and Financial Crimes Commission (EFCC) Act
- The Investment and Securities Act
- The Sectoral Codes of Corporate Governance notably, SEC Code, NCC Code, NAICOM Code, PENCOM Code and CBN Codes.
- The National/Nigerian Code of Corporate Governance (The National Code) which have superseded the sectoral codes.
- Adoption of the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB)
- Adoption of the International Standards on Auditing (ISA) issued by the International Auditing and Assurance Standards Board (IAASB).
Similar to the USA’s SOX Act section 404, the Nigerian Investment Acts, sections 60 to 63 and the National Code of Corporate Governance and the International Standards on Auditing (ISA) emphasized the need to incorporate robust fraud risk assessment in both the external and internal audit engagement lifecycles to help the auditors develop broad view of the fraud risk exposures and potential implications to determine the audit responses that are required to conduct productive audit delivery. Also, the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) emphasized the need for the accountants to pay attention to fraud risks and the anti-fraud internal controls.
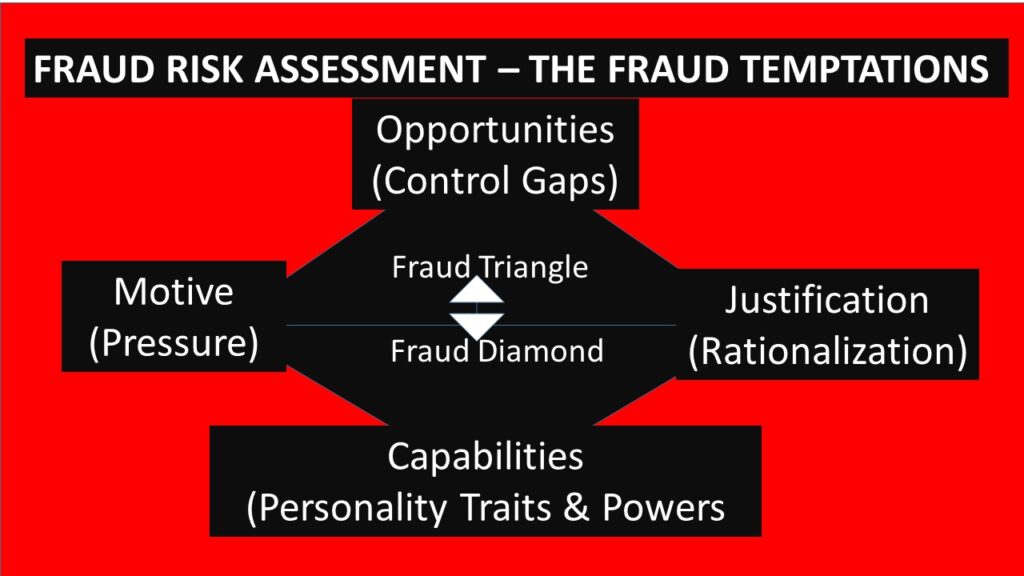


The blog touched relevant knowledge elements but it is too long. Concise blogs pass messages quicker.
Dear Edu
Thanks for the comment. Your recommendations noted.