How Internal Audit Can Help
Internal Auditing is a strategic component of good corporate governance and business management designed to provide independent, objective assurance and advisory to the board, management and support functions in all the relevant aspects of the company’s business.
Simply put in a mathematical equation: Internal Auditing = Value Protection + Value Addition
The value protection comes from the quality of audit findings, conclusions and audit opinions.
Value addition comes from the quality of the audit recommendations, the improvements they bring, and insights provided on the opportunities to be maximizeed to meet the current and future business needs.
To achieve these mandates, the internal auditors must adopt Process excellence + Personal excellence + Professional Excellence + Organizational excellence in their work performance delivery.
Process excellence criteria
Process excellence means that the internal audit function should adopt effective and efficient policies, processes and standard operating procedures in their work performance delivery from planning to completion and reporting.
Below is a pictorial presentation of a typical internal audit management Lifecyle providing examples of the different activity stages typically involved in the internal audit work performance delivery.
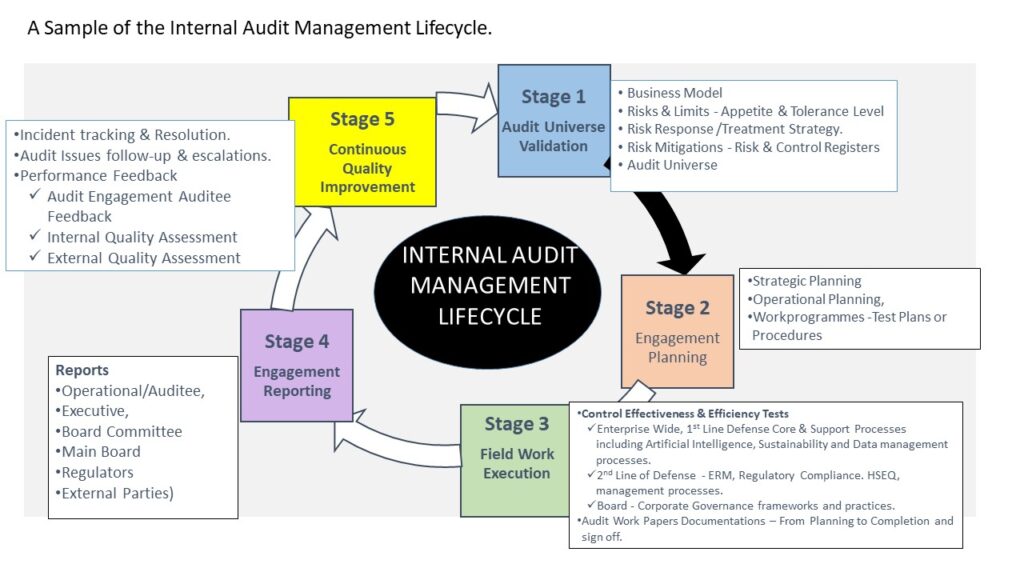
Professional excellence criteria
Professional excellence requires that the internal auditors must understand the relevant laws, regulatory guidelines and industry standards applicable to the internal audit profession and their organizations. In Nigeria, some of the laws (acts), regulatory guidelines and international industry standards applicable to companies and ineternal audit professiona are the following:
- Companies and Allied Matters Act (CAMA) 2020 and amendments,
- Investment and Secuities Act (ISA) 2017 and SEC Guidelines, and amendments,
- Financial Reporting Council Act (FRC) 2011, Guidelines and Amendments including ICFR and National Code of Corporate Governance.
- CBN Act and guidelines and circulars for Banks and Discount Houses,
- PENCOM Act and guidelines for Pension Fund administrators and Custodians
- NAICOM Act and guidelines for the insurance industries
- NCC Act and guidelines for the telecom industries
- IIIA Global for the Internal Audit profession.
- Other Self Regulated Organizations such as CIBN, ICSAN, ICAN, etc.
The responsibilities of the internal auditors are to ensure that they understand these applicable laws and their company’s compliance status.
In most organizations, the regulatory compliance function or company secretariate in collaboration with the legal department are responsible for the monitoring of their company’s compliance status and reporting to the regulators. The internal audit function should ensure that the regulatory compliance function is audited by the internal audit team to ensure that the regulatory compliance department are up to speed and follow dues processes in performance of their roles.
Organizational Excellence criteria
Organizational excellence requires that the internal audit function must understand the business model of their organization. They must understand the following:
- Organisational purpose – vision, mission, core values, value propositions
- Strategic directions – strategic thrusts (long term goals and objectives, business priorities, external and internal factors generating risk events in the business and mechanisms put in place by board and management to effectively respond to the risks and stir the company to the right directions.
- The internal audit function must also audit the risk management, internal control and HSEQ functions to ensure that they apply the right best practices standards & frameworks in supporting their core and support business functions in identifying, quantifying, ranking and prioritizing, mitigating, monitoring and reporting the various risk categories (strategic, operational, regulatory, financial and non-financial risks events) and taking appreciate actions in line with the risks limits (appetite and tolerance levels).
- Below are a pictorial representation of a typical business model and the key elements that internal auditors can consider in delivering audit engagements.
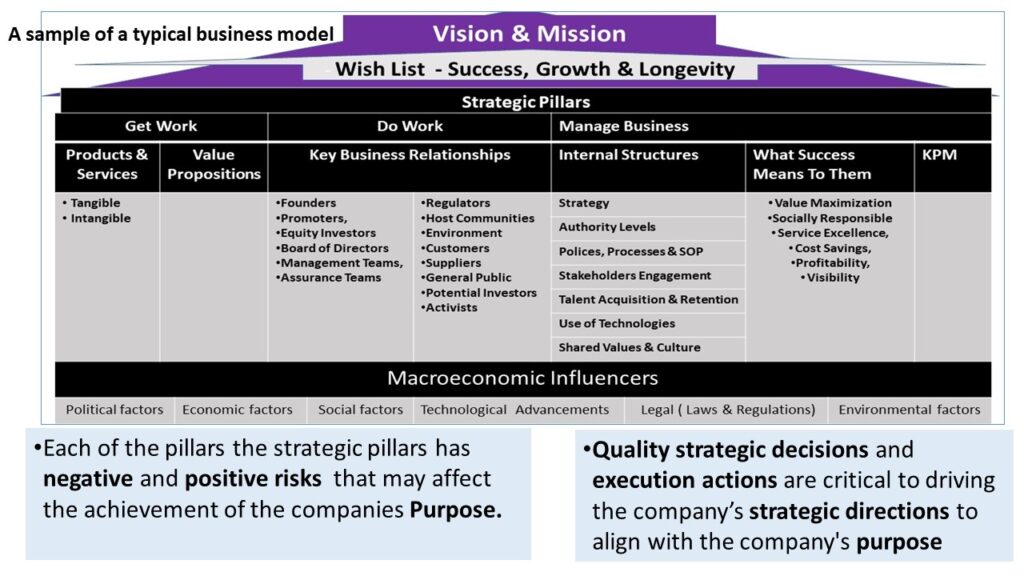
The internal auditors should leverage their understanding of the business model and applicable laws, the internal audit functions should plan the execution of their internal audit through the following:
- Validate the business priorities and issues that keep the board and management awake at night
- Build the internal audit universe
- Develop robust internal audit strategic plan to drive the annual (operational) audit plan and field work execution.
- Execute audit field work based on the operational Internal Audit plan by developing standard audit work programmes for each audit engagement,
- Collect the required audit evidence through manual and automated controls reviews, data analytics, ITGC, SaaS applications, AI, ESG
- Document working papers for future referencing and audit reperformance.
- Prepare unbiased and objective audit (truth based) reports for the various management and governance levels (operational report for the audits, Executive Summary for the executive management, Board Audit Committee and Board Park for Board Meeting. The report should highlight audit findings, conclusions, opinions and SMART improvement recommendations to address the gaps and optimize opportunities for moving the company forward.
- Perform post audit follow-ups to ensure that audit issues are properly and timely closed by the various responsible and accountability roles.
- Ensure that internal quality assessment is performed by Internal Audit and External Audit Quality Assessment is sponsored by the Board Audit Committee inline with the board approved frequency.
Personal excellence criteria
Personal excellence means that the internal auditors must demonstrate good soft skills in attitudes and behaviours and actions in all that they think, talk and do. Some of the key personal creditable attributes internal auditors should demonstrate include the following:
- Credibility,
- Reliability,
- Collaboration,
- Empathy,
- Commitment above self,
- Inquisitive Mindset,
- Self-Awareness ,
- Reflective ,
- Discerning and
- Focus on the Purpose and Strategic Directions to achieving the Purpose.
Examples of discreditable behaviours that IIA IPPF specified for Internal Auditors to avoid are
(a) Stating that the internal audit function is operating in conformance with the Global Internal Audit
(b) Standards when the assertion is not supported.
(c) Failing to accept responsibility for mistakes.
(d) Bullying, harassment, or discrimination.
(e) Lying, deceiving, or intentionally misleading others, including misrepresenting one’s competency or
qualifications (such as claiming to hold a certification or displaying credentials when the designation
is expired or inactive, has been revoked, or was never earned).
(f) Intentionally issuing false reports or communications or allowing or encouraging others to do so,
(g) including minimizing, concealing, or omitting internal audit findings, conclusions, or ratings from
engagement reports or overall assessments.
(h) Overlooking illegal activities that the organization may tolerate or condone.
(i) Soliciting or disclosing confidential information without proper authorization.
(j) Performing internal audit services with undeclared impairments to objectivity or independence.
(k) Failing to accept responsibility for mistakes.



Very insightful and helpful.
Thanks for what you are doing
Thanks you very much Chileobim for your inspiration. I appreciate